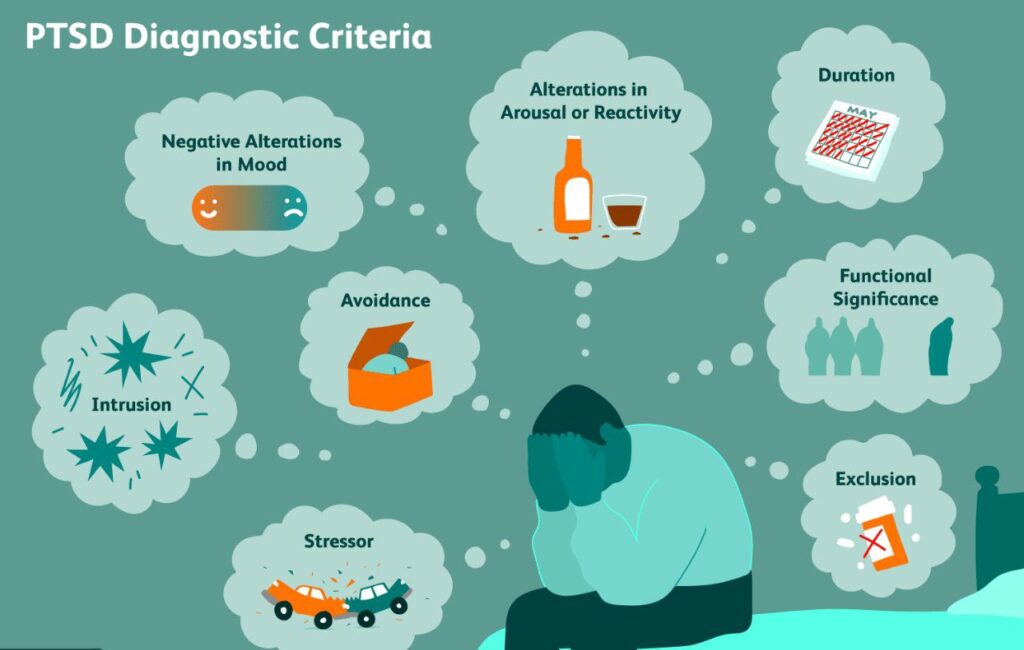
Understanding PTSD Across Cultures: A Global Perspective
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex and debilitating mental health condition that can affect individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds. While the symptoms of PTSD are similar across cultures, the way in which it is experienced and expressed can vary significantly. In this article, we will explore the concept of PTSD across cultures, highlighting the importance of cultural sensitivity and awareness in diagnosis and treatment.
Prevalence of PTSD Across Cultures
Studies have shown that PTSD is a widespread condition that can affect people from all walks of life, regardless of their cultural background. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), PTSD affects an estimated 3.5% of the global population, with women being more likely to experience PTSD than men (Kessler et al., 2005). However, cultural differences in the expression of trauma and coping mechanisms can affect the prevalence and presentation of PTSD.
Cultural Factors Influencing PTSD
Several cultural factors can influence the development and expression of PTSD, including:
- Collectivist versus Individualist Cultures: In collectivist cultures, such as those found in many Asian and African societies, the individual’s sense of identity is often closely tied to their family or community. This can lead to a greater emphasis on social support and communal coping mechanisms, which may be less effective in reducing PTSD symptoms (Kim et al., 2013).
- Gender Roles: Cultural gender roles can also play a significant role in shaping PTSD experiences. For example, in some cultures, women may be expected to prioritize family and caregiving responsibilities over personal well-being, which can lead to increased stress and trauma (Kirmayer et al., 2007).
- Trauma Types: The type of trauma experienced can also vary across cultures. For example, in war-torn countries, physical trauma may be more prevalent, while in countries with high levels of violence or social unrest, emotional trauma may be more common (Hobfoll et al., 2007).
Cultural Considerations in Diagnosis and Treatment
Given the cultural nuances surrounding PTSD, it is essential to consider these factors when diagnosing and treating patients. Here are some key considerations:
- Assessment Tools: Standardized assessment tools may not be culturally sensitive or applicable to all populations. Clinicians should use culturally adapted tools or develop new ones that take into account local cultural norms and values.
- Language Barriers: Language barriers can be a significant obstacle to diagnosis and treatment. Clinicians should strive to provide interpreters or use technology-based solutions to facilitate communication.
- Cultural Competence: Clinicians should aim to develop cultural competence by learning about the patient’s cultural background, values, and beliefs. This can help build trust and facilitate effective communication.
- Traditional Healing Practices: Many cultures have traditional healing practices that can be used in conjunction with Western therapies. Clinicians should be open to exploring these practices and incorporating them into treatment plans where possible.
Conclusion
PTSD is a complex condition that affects individuals across cultures and societies. Understanding the cultural nuances surrounding PTSD is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. By acknowledging the importance of cultural sensitivity and awareness, clinicians can provide more personalized and effective care for patients from diverse cultural backgrounds.
References:
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
Social, cultural, and other diversity issues in the traumatic stress field – PMC (nih.gov)
Psychiatry.org – What is Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
Websites:
Britmed Healthcare: https://britmedhealthcare.co.uk/
Nightingale Hospital: https://www.nightingalehospital.co.uk/
Top Doctors: https://www.topdoctors.co.uk/doctor/ahmed-el-missiry
You can also book, Contact us on WhatsApp 08009708017